Note: Bump mapping with non-diffuse materials does not work correctly, and smoothed normals will be flat when using a bump map.
extruded_path(
points,
x = 0,
y = 0,
z = 0,
polygon = NA,
polygon_end = NA,
breaks = NA,
closed = FALSE,
closed_smooth = TRUE,
polygon_add_points = 0,
twists = 0,
texture_repeats = 1,
straight = FALSE,
precomputed_control_points = FALSE,
width = 1,
width_end = NA,
width_ease = "spline",
smooth_normals = FALSE,
u_min = 0,
u_max = 1,
linear_step = FALSE,
end_caps = c(TRUE, TRUE),
material = diffuse(),
material_caps = NA,
angle = c(0, 0, 0),
order_rotation = c(1, 2, 3),
flipped = FALSE,
scale = c(1, 1, 1)
)Arguments
- points
Either a list of length-3 numeric vectors or 3-column matrix/data.frame specifying the x/y/z points that the path should go through.
- x
Default `0`. x-coordinate offset for the path.
- y
Default `0`. y-coordinate offset for the path.
- z
Default `0`. z-coordinate offset for the path.
- polygon
Defaults to a circle. A polygon with no holes, specified by a data.frame() parsable by `xy.coords()`. Vertices are taken as sequential rows. If the polygon isn't closed (the last vertex equal to the first), it will be closed automatically.
- polygon_end
Defaults to `polygon`. If specified, the number of vertices should equal the to the number of vertices of the polygon set in `polygon`. Vertices are taken as sequential rows. If the polygon isn't closed (the last vertex equal to the first), it will be closed automatically.
- breaks
Defaults to `20` times the number of control points in the bezier curve.
- closed
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, the path will be closed by smoothly connecting the first and last points, also ensuring the final polygon is aligned to the first.
- closed_smooth
Default `TRUE`. If `closed = TRUE`, this will ensure C2 (second derivative) continuity between the ends. If `closed = FALSE`, the curve will only have C1 (first derivative) continuity between the ends.
- polygon_add_points
Default `0`. Positive integer specifying the number of points to fill in between polygon vertices. Higher numbers can give smoother results (especially when combined with `smooth_normals = TRUE`.
- twists
Default `0`. Number of twists in the polygon from one end to another.
- texture_repeats
Default `1`. Number of times to repeat the texture along the length of the path.
- straight
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, straight lines will be used to connect the points instead of bezier curves.
- precomputed_control_points
Default `FALSE`. If `TRUE`, `points` argument will expect a list of control points calculated with the internal rayrender function `rayrender:::calculate_control_points()`.
- width
Default `0.1`. Curve width. If `width_ease == "spline"`, `width` is specified in a format that can be read by `xy.coords()` (with `y` as the width), and the `x` coordinate is between `0` and `1`, this can also specify the exact positions along the curve for the corresponding width values. If a numeric vector, specifies the different values of the width evenly along the curve. If not a single value, `width_end` will be ignored.
- width_end
Default `NA`. Width at end of path. Same as `width`, unless specified. Ignored if multiple width values specified in `width`.
- width_ease
Default `spline`. Ease function between width values. Other options: `linear`, `quad`, `cubic`, `exp`.
- smooth_normals
Default `FALSE`. Whether to smooth the normals of the polygon to remove sharp angles.
- u_min
Default `0`. Minimum parametric coordinate for the path. If `closed = TRUE`, values greater than one will refer to the beginning of the loop (but the path will be generated as two objects).
- u_max
Default `1`. Maximum parametric coordinate for the path. If `closed = TRUE`, values greater than one will refer to the beginning of the loop (but the path will be generated as two objects).
- linear_step
Default `FALSE`. Whether the polygon intervals should be set at linear intervals, rather than intervals based on the underlying bezier curve parameterization.
- end_caps
Default `c(TRUE, TRUE)`. Specifies whether to add an end cap to the beginning and end of a path.
- material
Default
diffuse. The material, called from one of the material functions.- material_caps
Defaults to the same material set in `material`. Note: emissive objects may not currently function correctly when scaled.
- angle
Default `c(0, 0, 0)`. Angle of rotation around the x, y, and z axes, applied in the order specified in `order_rotation`.
- order_rotation
Default `c(1, 2, 3)`. The order to apply the rotations, referring to "x", "y", and "z".
- flipped
Default `FALSE`. Whether to flip the normals.
- scale
Default `c(1, 1, 1)`. Scale transformation in the x, y, and z directions. If this is a single value, number, the object will be scaled uniformly.
Value
Single row of a tibble describing the cube in the scene.
Examples
if(run_documentation()) {
#Specify the points for the path to travel though and the ground material
points = list(c(0,0,1),c(-0.5,0,-1),c(0,1,-1),c(1,0.5,0),c(0.6,0.3,1))
ground_mat = material=diffuse(color="grey50",
checkercolor = "grey20",checkerperiod = 1.5)
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Default path shape is a circle
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.25,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
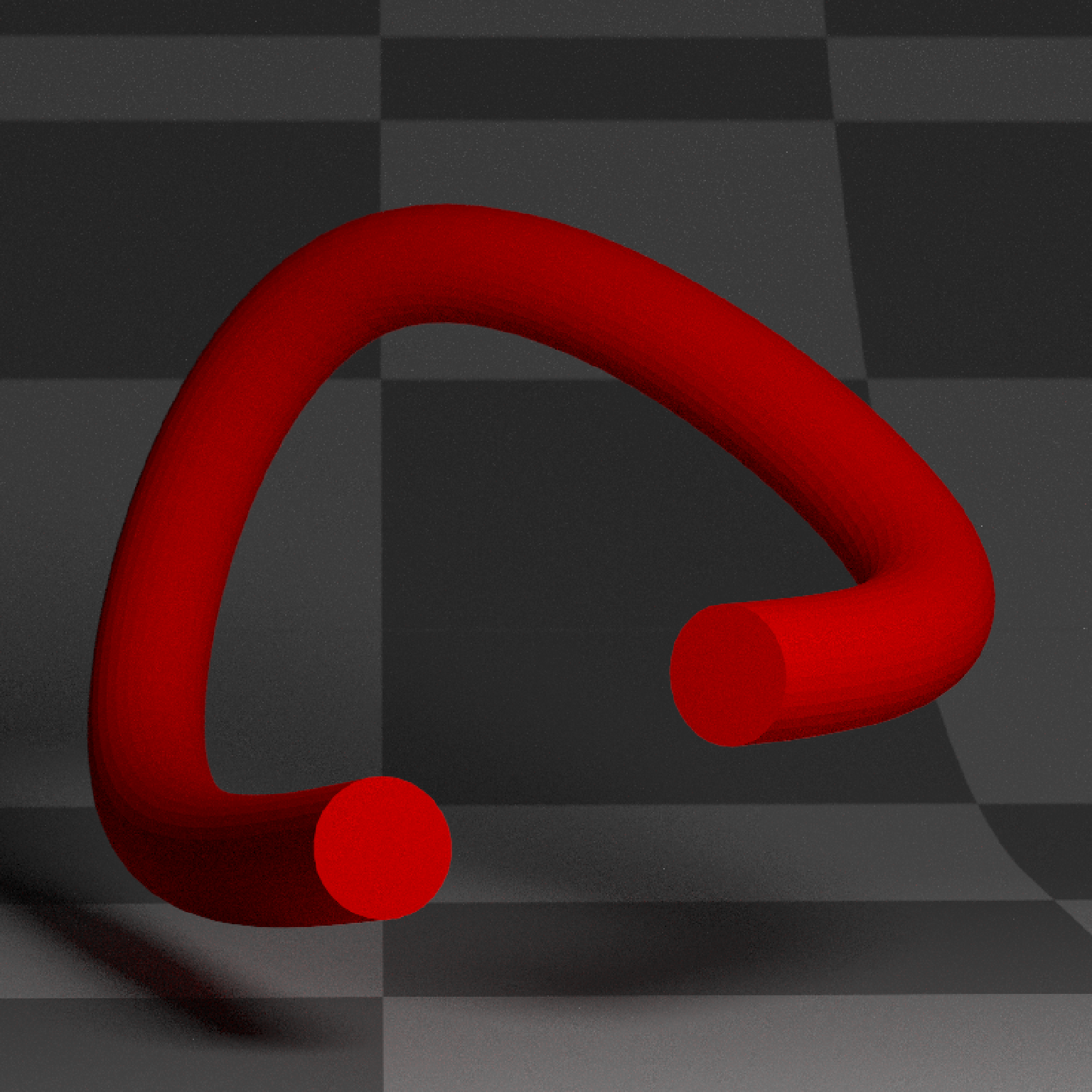 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the width evenly along the tube
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.25,
width_end = 0.5,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the width evenly along the tube
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.25,
width_end = 0.5,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
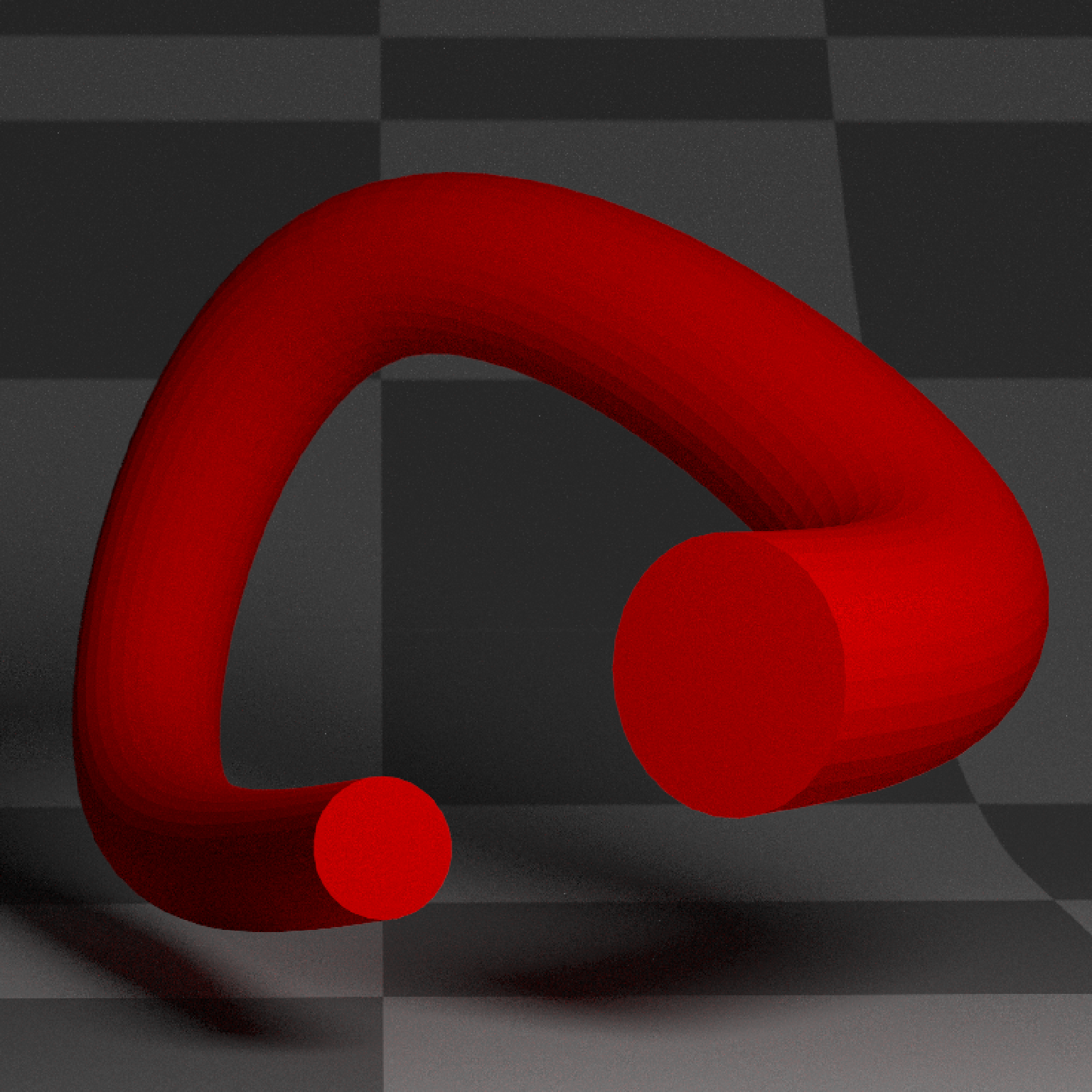 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the width along the full length of the tube
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points,
width=0.25*sinpi(0:72*20/180),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the width along the full length of the tube
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points,
width=0.25*sinpi(0:72*20/180),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
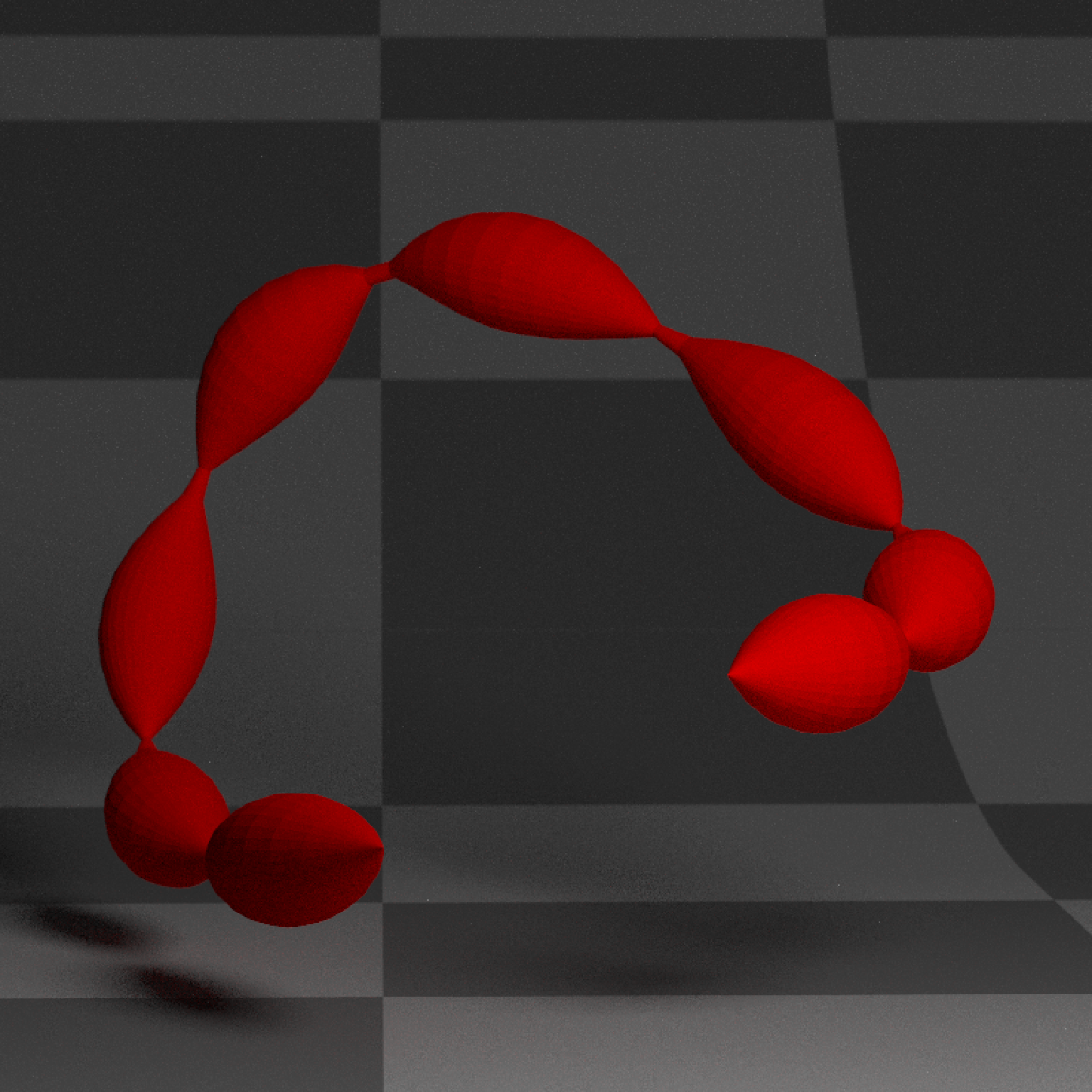 if(run_documentation()) {
#Specify the exact parametric x positions for the width values:
custom_width = data.frame(x=c(0,0.2,0.5,0.8,1), y=c(0.25,0.5,0,0.5,0.25))
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points,
width=custom_width,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Specify the exact parametric x positions for the width values:
custom_width = data.frame(x=c(0,0.2,0.5,0.8,1), y=c(0.25,0.5,0,0.5,0.25))
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points,
width=custom_width,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
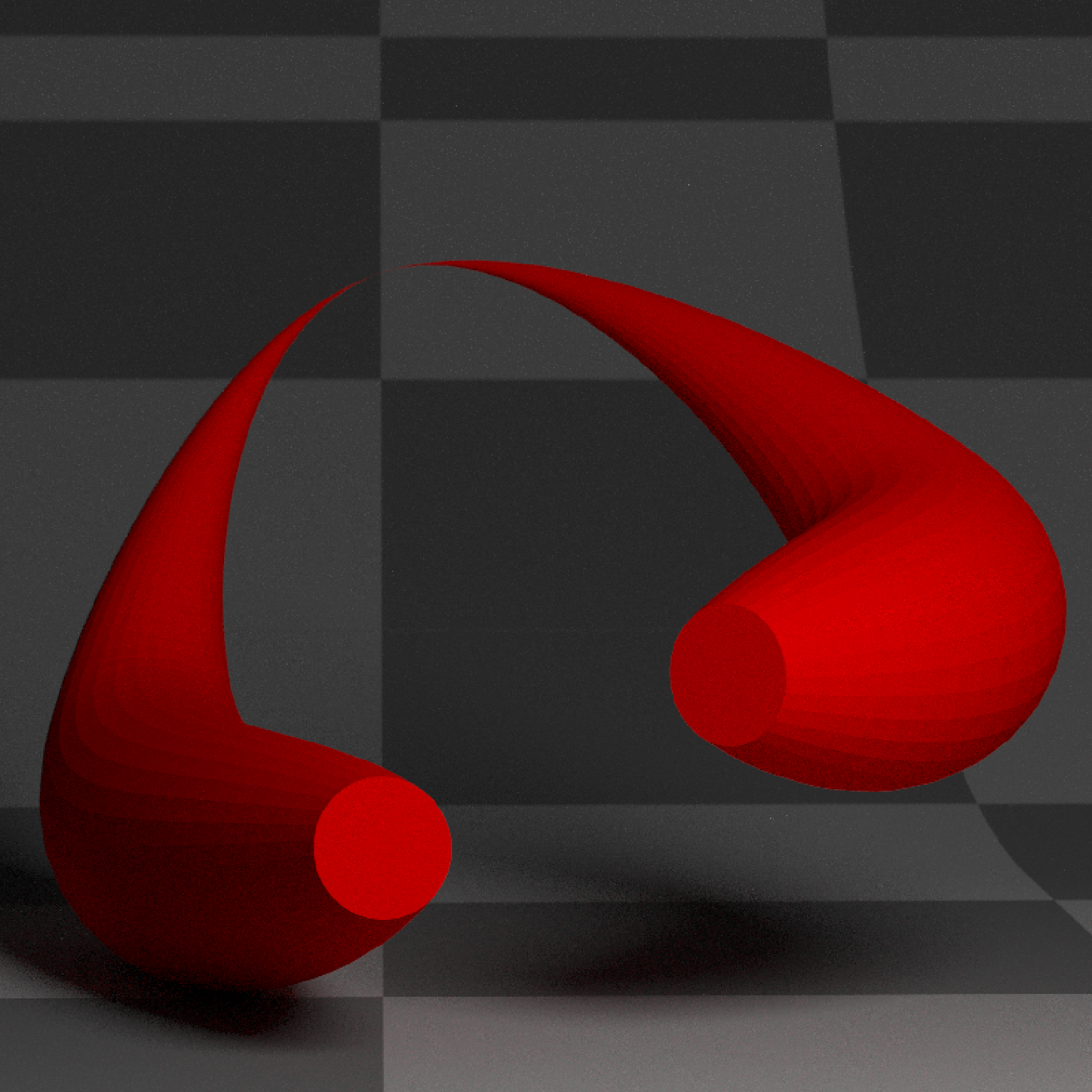 if(run_documentation()) {
#Generate a star polygon
angles = seq(360,0,length.out=21)
xx = c(rep(c(1,0.75,0.5,0.75),5),1) * sinpi(angles/180)/4
yy = c(rep(c(1,0.75,0.5,0.75),5),1) * cospi(angles/180)/4
star_polygon = data.frame(x=xx,y=yy)
#Extrude a path using a star polygon
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5,
polygon = star_polygon,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,1),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Generate a star polygon
angles = seq(360,0,length.out=21)
xx = c(rep(c(1,0.75,0.5,0.75),5),1) * sinpi(angles/180)/4
yy = c(rep(c(1,0.75,0.5,0.75),5),1) * cospi(angles/180)/4
star_polygon = data.frame(x=xx,y=yy)
#Extrude a path using a star polygon
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5,
polygon = star_polygon,
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,1),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
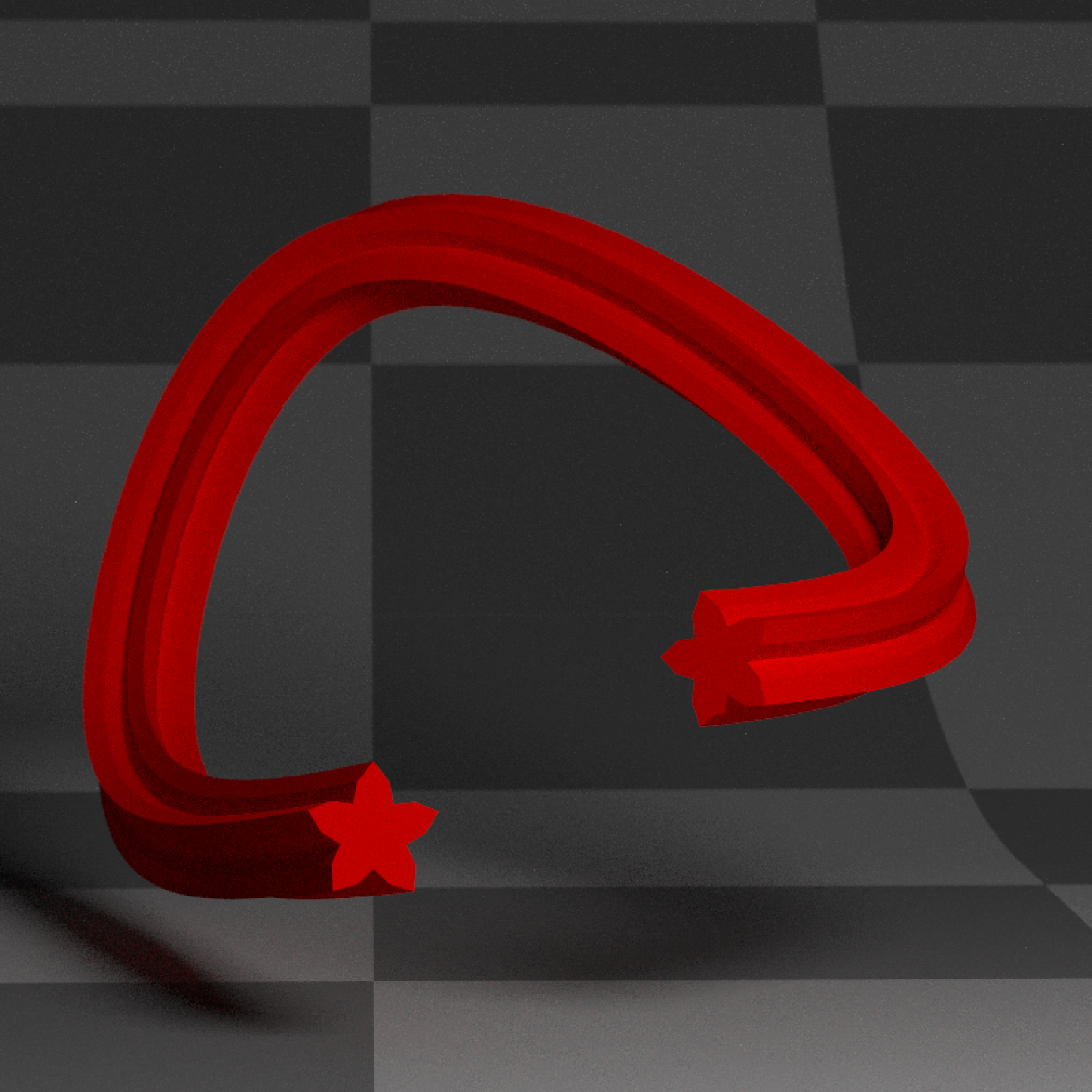 if(run_documentation()) {
#Specify a circle polygon
angles = seq(360,0,length.out=21)
xx = sinpi(angles/180)/4
yy = cospi(angles/180)/4
circ_polygon = data.frame(x=xx,y=yy)
#Transform from the circle polygon to the star polygon and change the end cap material
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5,
polygon=circ_polygon, polygon_end = star_polygon,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Specify a circle polygon
angles = seq(360,0,length.out=21)
xx = sinpi(angles/180)/4
yy = cospi(angles/180)/4
circ_polygon = data.frame(x=xx,y=yy)
#Transform from the circle polygon to the star polygon and change the end cap material
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5,
polygon=circ_polygon, polygon_end = star_polygon,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0.5),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
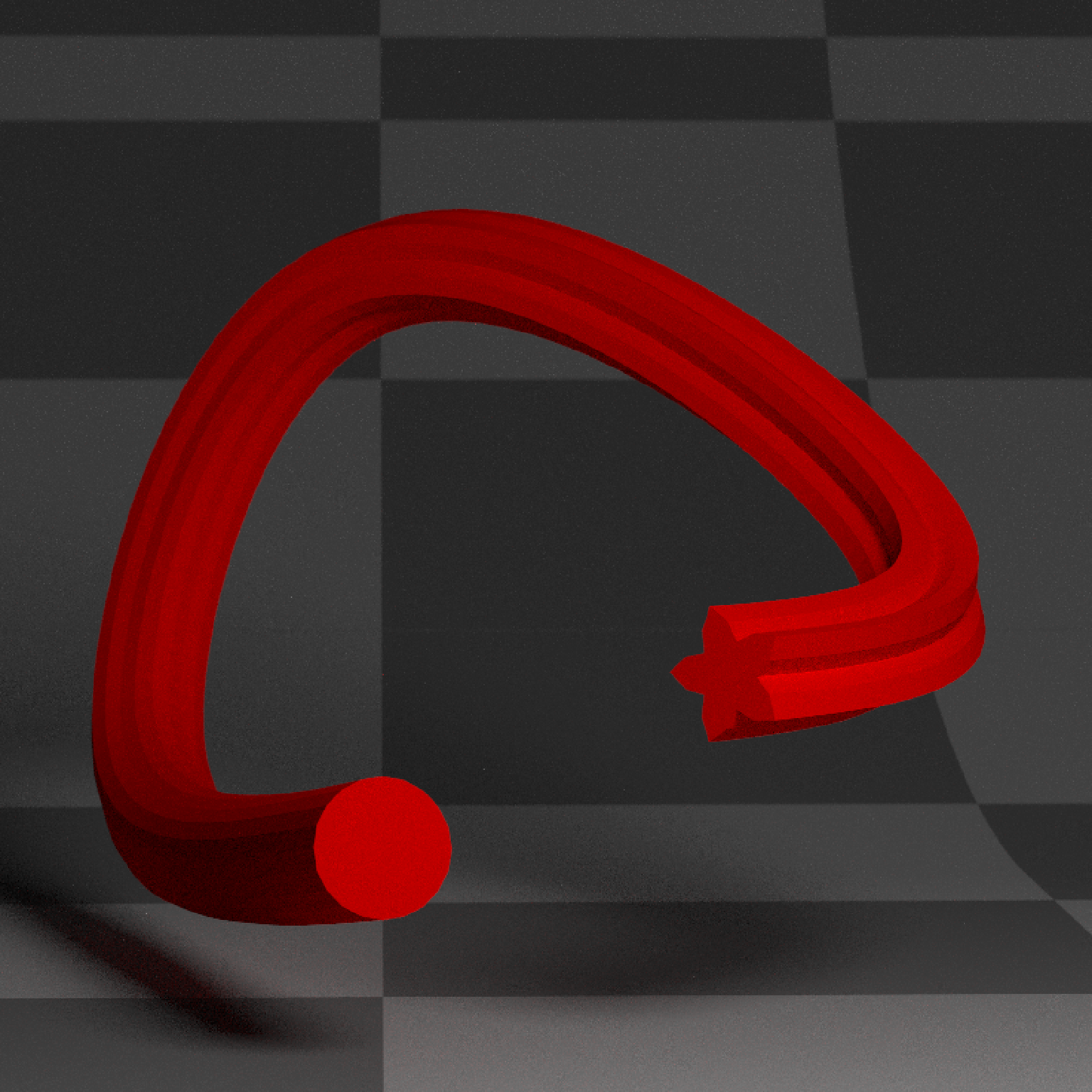 if(run_documentation()) {
#Add three and a half twists along the path, and make sure the breaks are evenly spaced
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
polygon=star_polygon, linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Add three and a half twists along the path, and make sure the breaks are evenly spaced
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
polygon=star_polygon, linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
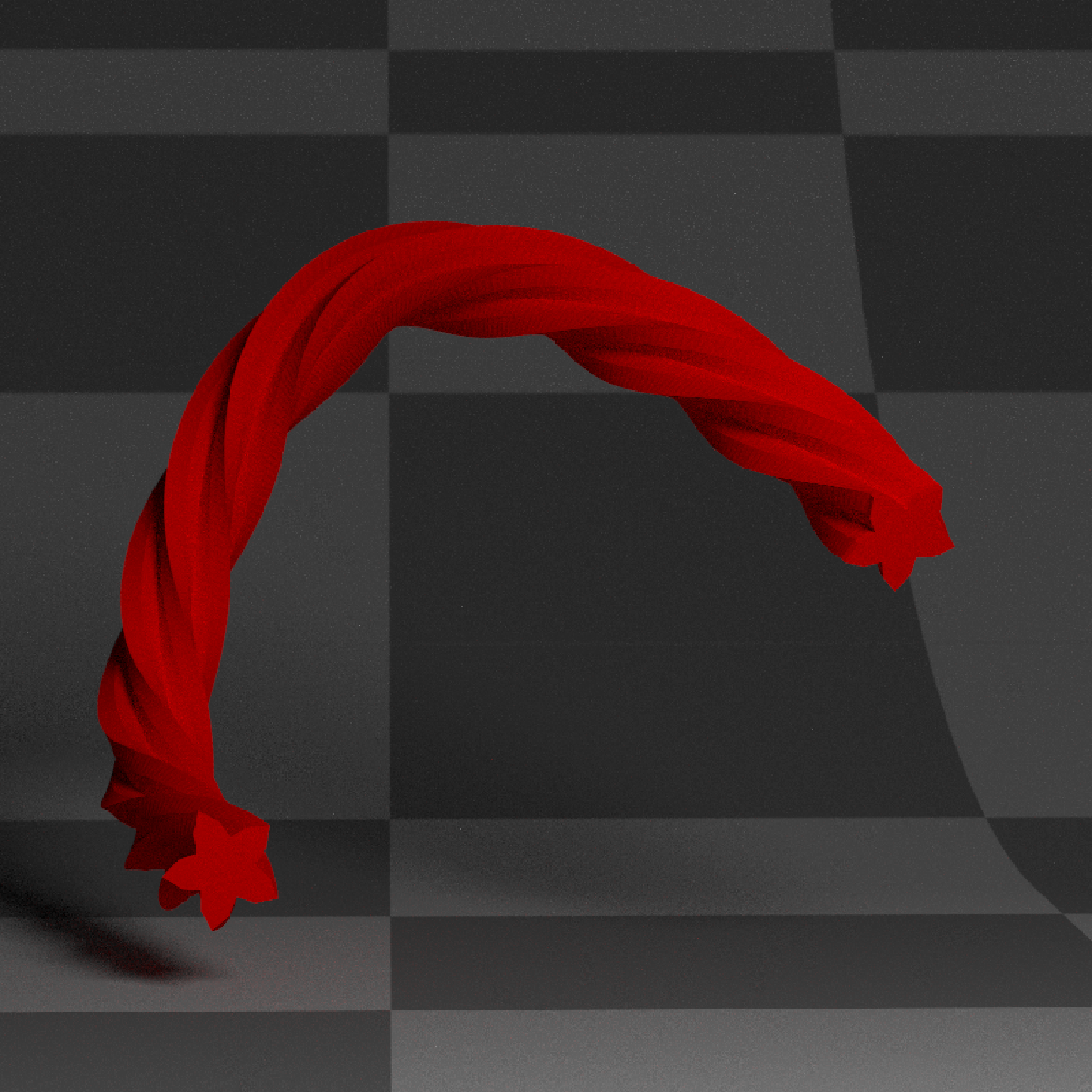
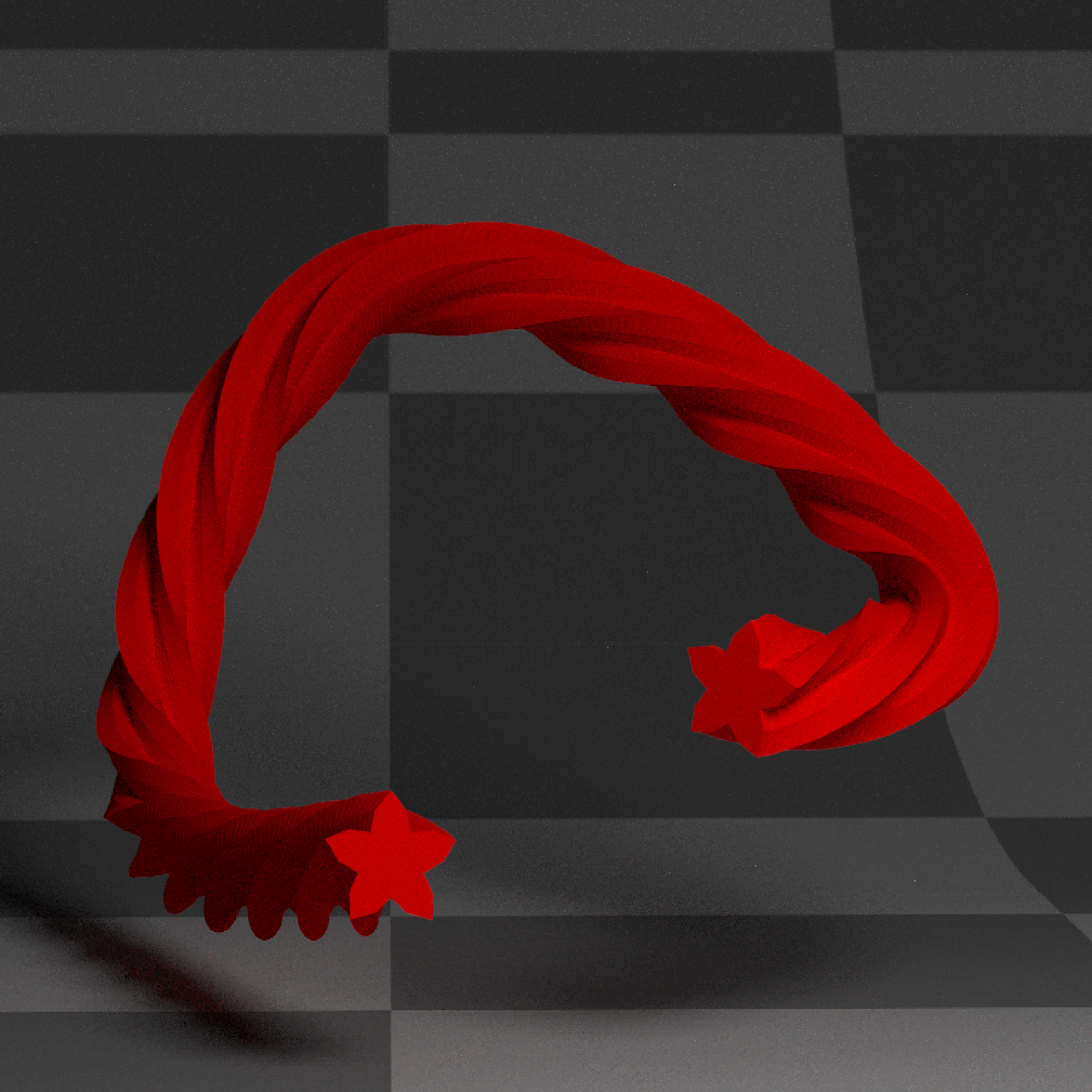 if(run_documentation()) {
#Smooth the normals for a less sharp appearance:
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
polygon=star_polygon,
linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
smooth_normals = TRUE,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Smooth the normals for a less sharp appearance:
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
polygon=star_polygon,
linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
smooth_normals = TRUE,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
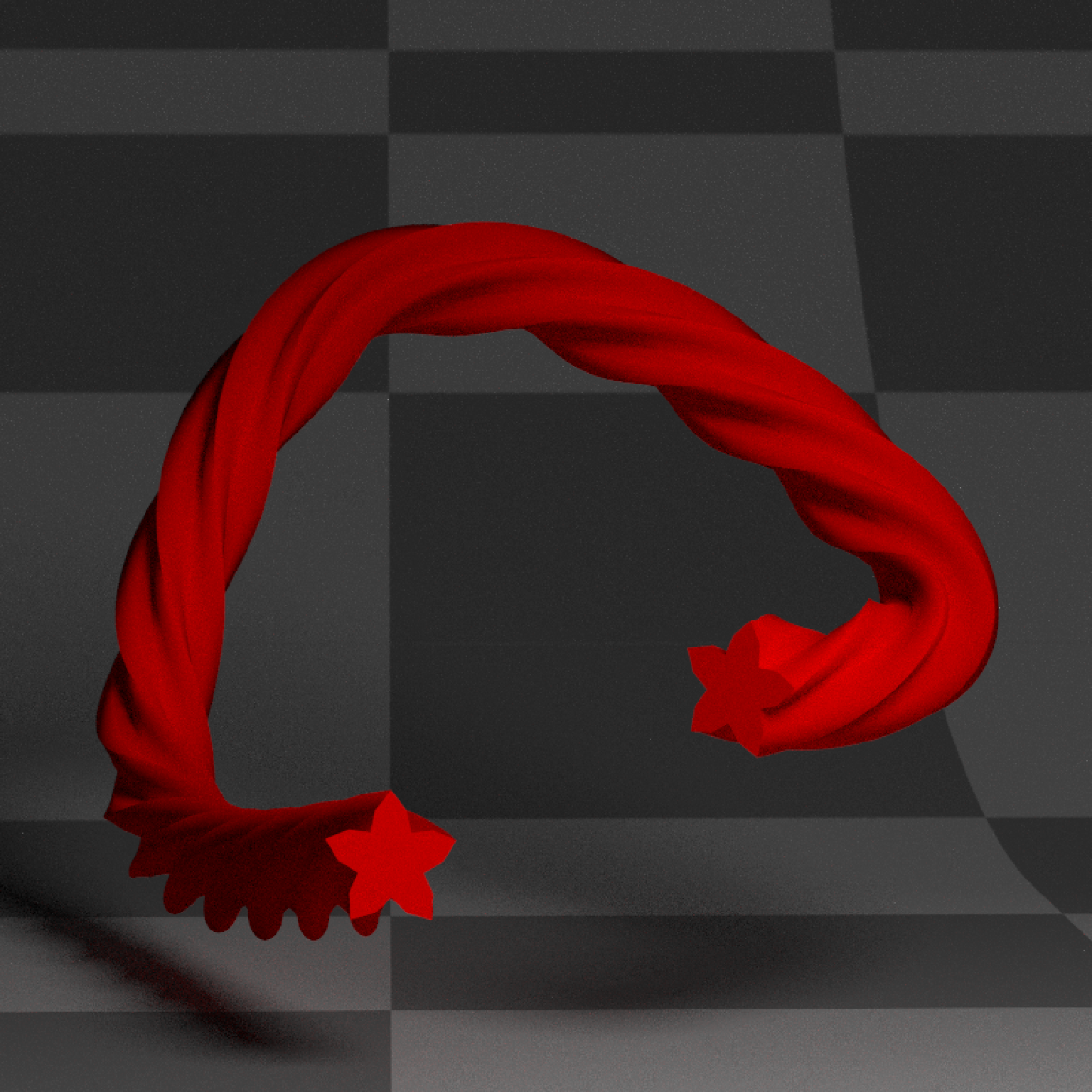 if(run_documentation()) {
#Only generate part of the curve, specified by the u_min and u_max arguments
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
u_min = 0.2, u_max = 0.8,
polygon=star_polygon, linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Only generate part of the curve, specified by the u_min and u_max arguments
generate_studio(depth=-0.4,material=ground_mat) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.5, twists = 3.5,
u_min = 0.2, u_max = 0.8,
polygon=star_polygon, linear_step = TRUE, breaks=360,
material_cap = diffuse(color="white"),
material=diffuse(color="red"))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=3,z=5,x=2,material=light(intensity=15))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0.3,0.5,0),fov=12, width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
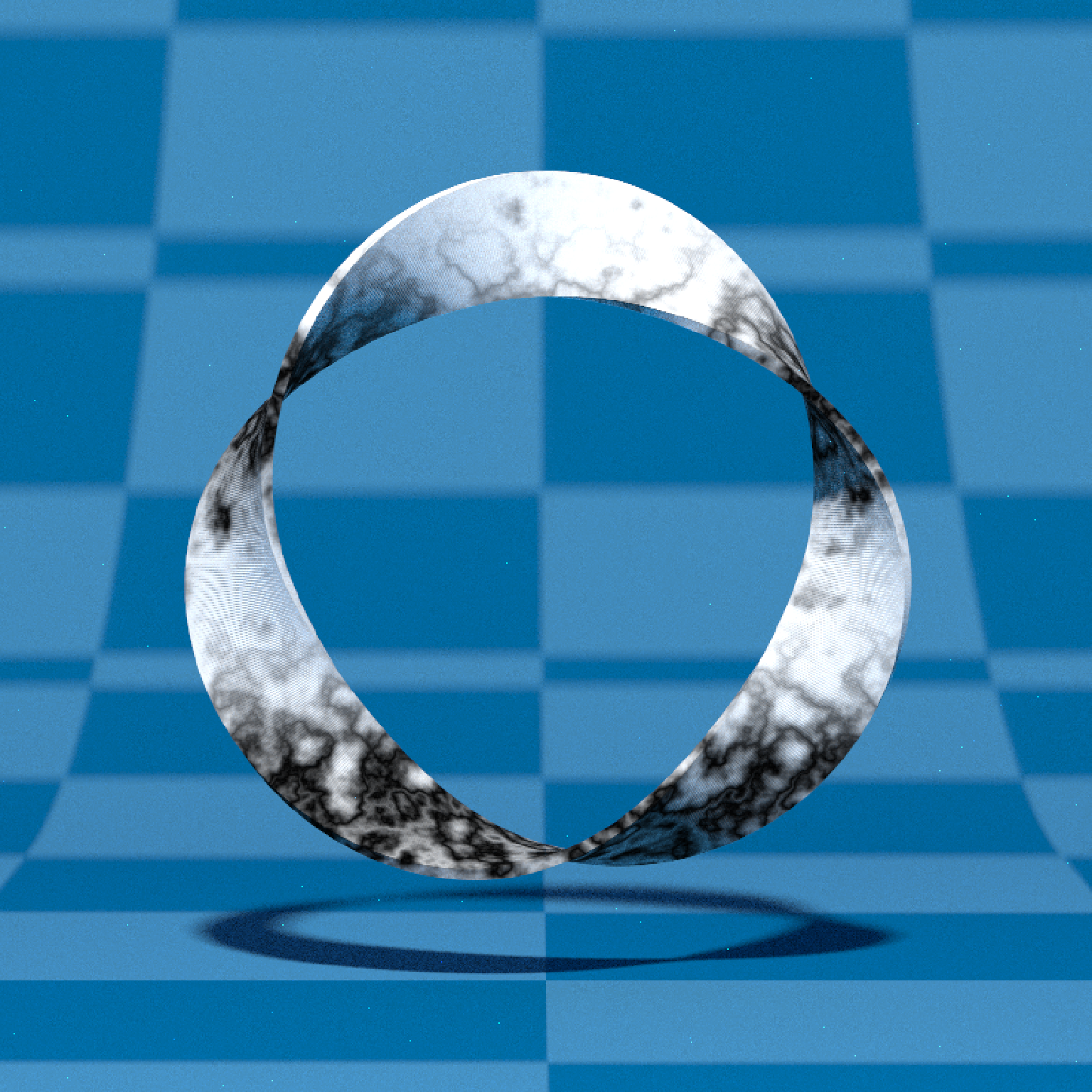
 if(run_documentation()) {
#Render a Mobius strip with 1.5 turns
points = list(c(0,0,0),c(0.5,0.5,0),c(0,1,0),c(-0.5,0.5,0))
square_polygon = matrix(c(-1, -0.1, 0,
1, -0.1, 0,
1, 0.1, 0,
-1, 0.1, 0)/10, ncol=3,byrow = T)
generate_studio(depth=-0.2,
material=diffuse(color = "dodgerblue4", checkercolor = "#002a61",
checkerperiod = 1)) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, polygon=square_polygon, closed = TRUE,
linear_step = TRUE, twists = 1.5, breaks = 720,
material = diffuse(noisecolor = "black", noise = 10,
noiseintensity = 10))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=20,x=0,z=21,material=light(intensity = 1000))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0,0.5,0), fov=10, samples=16, sample_method = "sobol_blue",
width = 800, height=800)
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Render a Mobius strip with 1.5 turns
points = list(c(0,0,0),c(0.5,0.5,0),c(0,1,0),c(-0.5,0.5,0))
square_polygon = matrix(c(-1, -0.1, 0,
1, -0.1, 0,
1, 0.1, 0,
-1, 0.1, 0)/10, ncol=3,byrow = T)
generate_studio(depth=-0.2,
material=diffuse(color = "dodgerblue4", checkercolor = "#002a61",
checkerperiod = 1)) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, polygon=square_polygon, closed = TRUE,
linear_step = TRUE, twists = 1.5, breaks = 720,
material = diffuse(noisecolor = "black", noise = 10,
noiseintensity = 10))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=20,x=0,z=21,material=light(intensity = 1000))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0,0.5,0), fov=10, samples=16, sample_method = "sobol_blue",
width = 800, height=800)
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
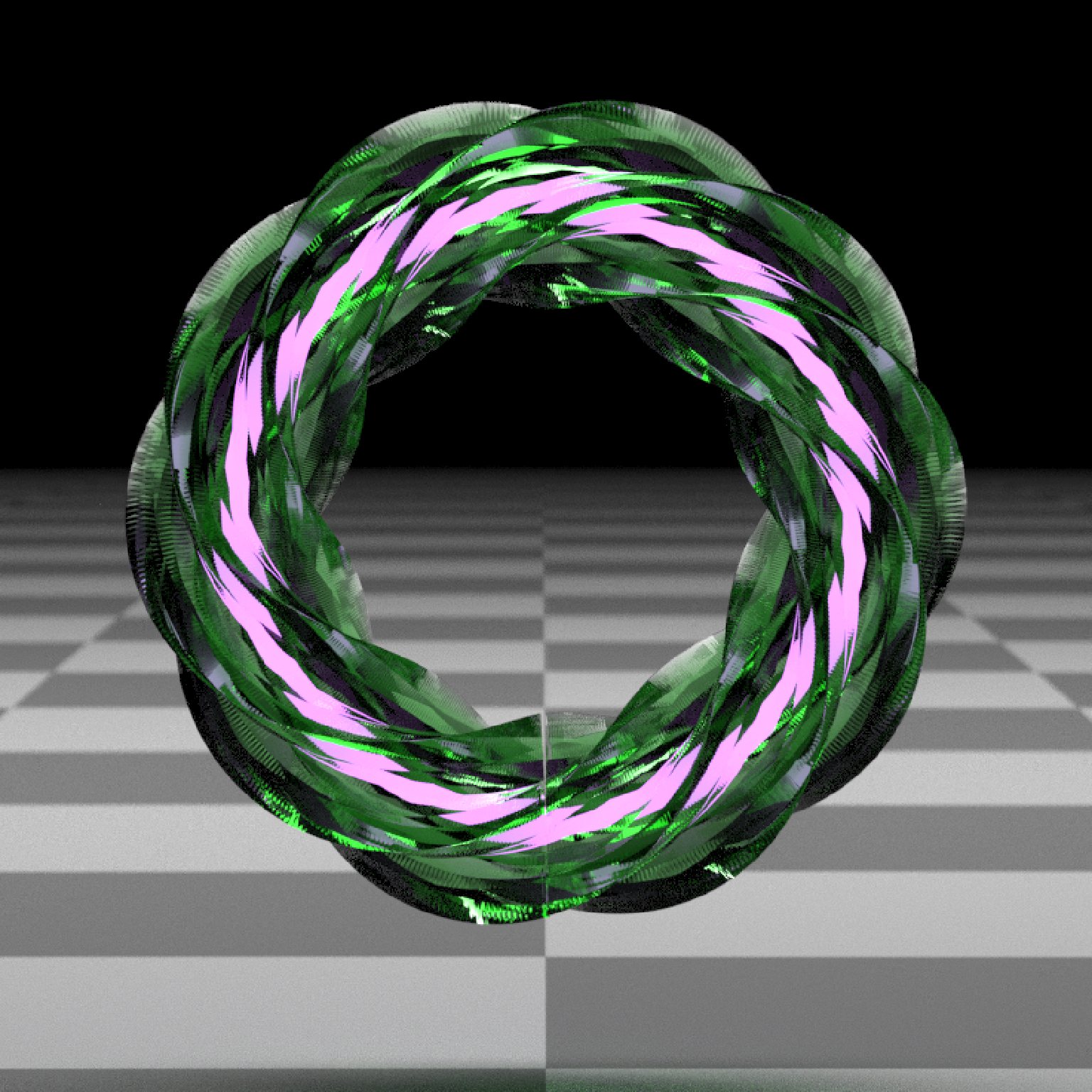
 if(run_documentation()) {
#Create a green glass tube with the dielectric priority interface
#and fill it with a purple neon tube light
generate_ground(depth=-0.4,material=diffuse(color="grey50",
checkercolor = "grey20",checkerperiod = 1.5)) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.7, linear_step = TRUE,
polygon = star_polygon, twists = 2, closed = TRUE,
polygon_end = star_polygon, breaks=500,
material=dielectric(priority = 1, refraction = 1.2,
attenuation=c(1,0.3,1),
attenuation_intensity=20))) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.4, linear_step = TRUE,
polygon = star_polygon,twists = 2, closed = TRUE,
polygon_end = star_polygon, breaks=500,
material=dielectric(priority = 0,refraction = 1))) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.05, closed = TRUE,
material=light(color="purple", intensity = 5,
importance_sample = FALSE))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=10,z=-5,x=0,radius=5,material=light(color = "white",intensity = 5))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0,0.5,1),fov=10,
width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Create a green glass tube with the dielectric priority interface
#and fill it with a purple neon tube light
generate_ground(depth=-0.4,material=diffuse(color="grey50",
checkercolor = "grey20",checkerperiod = 1.5)) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.7, linear_step = TRUE,
polygon = star_polygon, twists = 2, closed = TRUE,
polygon_end = star_polygon, breaks=500,
material=dielectric(priority = 1, refraction = 1.2,
attenuation=c(1,0.3,1),
attenuation_intensity=20))) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.4, linear_step = TRUE,
polygon = star_polygon,twists = 2, closed = TRUE,
polygon_end = star_polygon, breaks=500,
material=dielectric(priority = 0,refraction = 1))) %>%
add_object(extruded_path(points = points, width=0.05, closed = TRUE,
material=light(color="purple", intensity = 5,
importance_sample = FALSE))) %>%
add_object(sphere(y=10,z=-5,x=0,radius=5,material=light(color = "white",intensity = 5))) %>%
render_scene(lookat=c(0,0.5,1),fov=10,
width=800,height=800, clamp_value = 10,
aperture=0.025, samples=16, sample_method="sobol_blue")
}
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
#> Warning: material set as vertex color but no texture or bump map passed--ignoring mesh3d material.
